Norton Internet Security 2011 Crack 88 Years Ago
How To Use Crack:1. Entered in the Settings menu on the Norton Internet Security 20112. Select Miscellaneous Settings and look for product security3. Gramatica william cereja do rio.
- Norton Internet Security 2011 Crack 88 Years Ago Lyrics
- Norton Internet Security 2011 Crack 88 Years Ago Free
In the Norton Product Protection Temper should always turn off4. Install Crack 88 Years, click Ok to finish, if already completed 88 Years Crack will close itself.5.
Congratulations use Norton Internet Security 2011 with a subscription to 88 years.It should be noted1. Do not ever close the Crack 88 Years until the installation is complete.2. Each update Norton Internet Security 2011 (Run LiveUpdate), you must install the Crack 88 Years.3. Norton Product Protection Temper should always turn off.
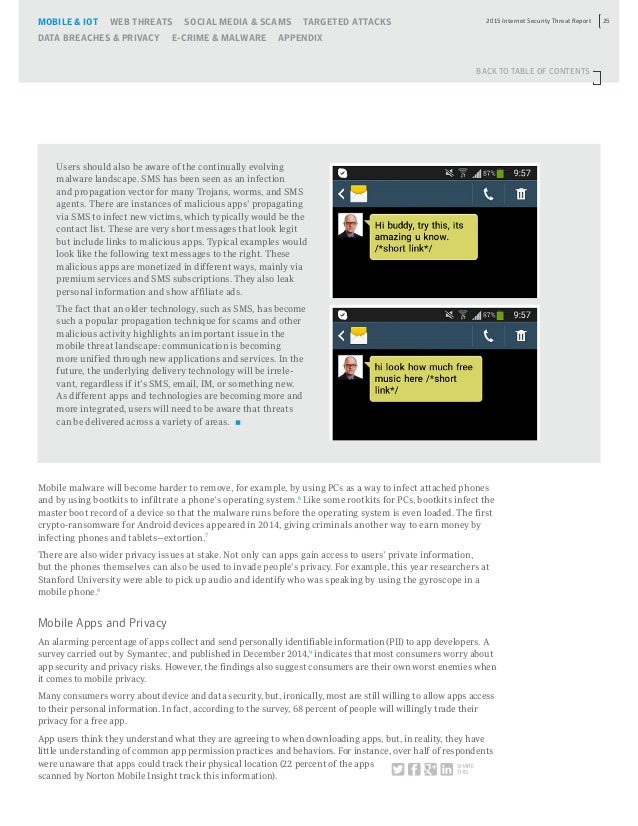
Viruses, hacking, Wi-Fi piggybacking, scams.staying as secure as possible online in 2019 is a complicated job and one that requires a new way of thinking.10 years ago, you could have limited your exposure to danger by simply staying offline. As times move on, however, there are fewer and fewer tasks and interactions that can be carried out offline.The number of errands that need the internet is growing every day, and it’s increasingly likely that a huge number of your “everyday” jobs – like shopping, banking, communicating and interacting with authorities and companies – are carried out online.Let’s take a look at some of the most common online security concerns, and how best to tackle them. PhishingPhishing is a fraudulent attempt to get or access from a person, usually over fake emails. This information might then be used to commit crimes or spread malware. The threat has been around for years (think of all those princes just giddy to give you money!), though modern phishing scams are far more sophisticated.Phishing usually comes in the form of an email, SMS, or website pop-up from a company or person you trust. Once you engage, they’re likely to ask you to hand over personal details (information) or click on a link or download a file (malware).
Phishing preventionThe best way to prevent is to think hard about incoming requests. Does this company usually email you? Do you even have an account with them? Is this the address or phone number you gave this company to communicate with you?Be highly suspicious of any email that asks you to do something, such as call them, log into your account, download a file, or click a link. Be extra suspicious of any urgency or drama in the communication – it’s trying to get you to act out of panic, without thinking.If you do click a link or download a file, your should spring into action and warn you of the dangers.
Similarly, if someone does get access to an account or online service using your details, having multifactor authentication enabled (requiring two or more steps to access an account) will most likely stop them in their tracks. Hackingis an interesting option since it is far less likely to affect you as an individual, even though the term is pretty much shorthand for “doing evil on the internet”. Many hackers are often professionals who go after high-profile targets.It goes without saying that the average computer user is unlikely to be hacked. Where hacking might affect you, however, is when companies that you do business with are hacked. This is known as a “” and there’s a good chance it’s already happened to you or someone you know at some point.
In this case, some of your information is leaked to a third party, who in turn uses it to do things they’re not supposed to.If a company is breached, they will likely contact you and let you know what you need to do to secure your information. It’s annoying, but a modern fact of life and there’s relatively little you can do about it beyond using separate passwords for separate accounts and choosing to only do business with companies which prioritise online security. Malwareand viruses are a traditional online problem that still present a significant risk to people who use the internet. Most infections will be caught via infected files or malicious links, which is how they’ve always been transmitted. What has changed, however, is what these viruses do.Many modern viruses are literally following the money – they instruct your computer to do things that will make them a profit.

Just causing havoc isn’t really on the cards anymore. A perfect example of this is “cryptojacking” or “pharming”, which is where your device is turned into a zombie computer that mines cryptocurrency on someone else’s behalf.Malware is pretty sneaky stuff, and you can pick it up in the most innocuous-looking of places. Can come packed into innocent-looking apps from the app store, silly-looking pop-ups on websites, or even in fake games that your kids might accidentally download.Preventing malwareWithout a doubt, the best way to protect your device from malware is to make sure there is an up-to-date installed on your device.
Norton Internet Security 2011 Crack 88 Years Ago Lyrics
Secondly, ensure that the devices themselves are updated as older devices and operating systems are easier to infect.On a more personal level, think and teach your family to think too. Never click on pop-ups and read app descriptions carefully to ensure that they seem legit and well-regarded. Just because something says it is a certain app, programme, or game doesn’t mean it is, so make sure you take contextual clues, like reading the description, reviews, URL, and download link to make sure you’re getting what you expect, even on official websites or stores.Wi-Fi threatsWhen it comes to security problems relating to Wi-Fi, we can divide the category into two clear halves – the risks you face at home (piggybacking and hacking) and the. At homeAt home, there is a risk that someone might “hack” your Wi-Fi. In the best case scenario, they just want to get your fast internet for free but in the worst, they want to use your Wi-Fi to hack into your computer, phone, or home network. Luckily, the way to help prevent both is simple: good, strong and up-to-date protection. The first will hopefully foil any attempts to gain access, and the second will detect the intruder if they do!On public Wi-FiOut and about, you should avoid public Wi-Fi where possible.
If you do connect, be aware that when using someone else’s Wi-Fi connection (sure, it’s called “Starbucks Free Wi-Fi”, but it could belong to anyone!), everything you do on that connection is funnelled through someone else’s computer – your bank details, emails, website logins, etc.Prevent this by installing a, which creates a barrier between your activity and the provider of the Wi-Fi. If you haven’t got a VPN on a given occasion, you’re going to have to fire up your security suite, cross your fingers and, please, don’t even think of logging into your online banking!Online securityOnline security is all about staying alert on various fronts and acting proactively.Sure, accidents and incidents will happen, but the same can be said for offline life and, as we can see, the distance between online and offline is closing every day.In short, you need internet security software because hackers and cybercriminals have an evolving rota of tricks in their bag. Cyberthreats are dangerous, but they can be avoided in five short steps:. Use security software where possible. Use a password manager to generate strong passwords. Enable multifactor authentication ( 2-step authentication) where possible.
Don’t use public Wi-Fi. Think and teach your loved ones to think!A. While being smart goes a long way, a security suite is an extra precaution for helping keep your precious information secure. Copyright © 2019 Symantec Corporation. All rights reserved.
Symantec, the Symantec Logo, the Checkmark Logo, Norton, Norton by Symantec, LifeLock, and the LockMan Logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Symantec Corporation or its affiliates in the United States and other countries. Firefox is a trademark of Mozilla Foundation. Google Chrome and Android are trademarks of Google, LLC. Mac, iPhone and iPad are trademarks of Apple Inc.
Norton Internet Security 2011 Crack 88 Years Ago Free
Microsoft and the Windows logo are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. The Android robot is reproduced and/or modified from work created and shared by Google and used according to terms described in the Creative Commons 3.0 Attribution License. Other company names and product names are registered trademarks or trademarks of each company.